Conceptual implementation¶
The mOTUs tool performs taxonomic profiling of metagenomics and metatrancriptomics samples, i.e. it identifies species and their relative abundance present in a sample. It is based on a set of mOTUs (~species) contained in the mOTUs database. The mOTUs database is created from reference genomes, metagenomic samples and metagenome assembled genomes (MAGs):
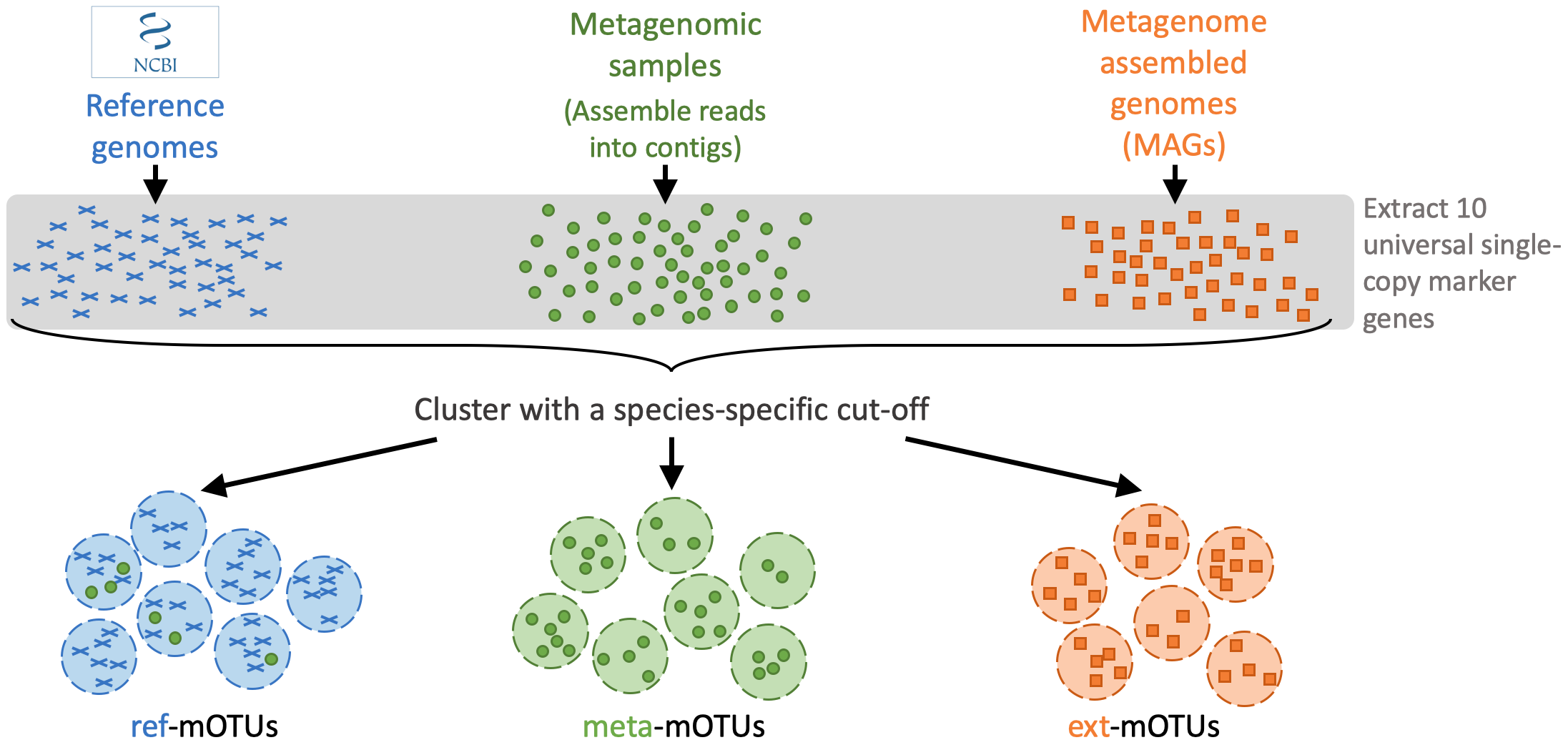
A mOTUs database is composed of three types of mOTUs:
ref-mOTUs, which represent known species,
meta-mOTUs, which represent unknown species obtained from metagenomic samples,
ext-mOTUs, which represent unknown species obtained from MAGs.
Note that meta- and ext-mOTUs will not have a species level annotation.
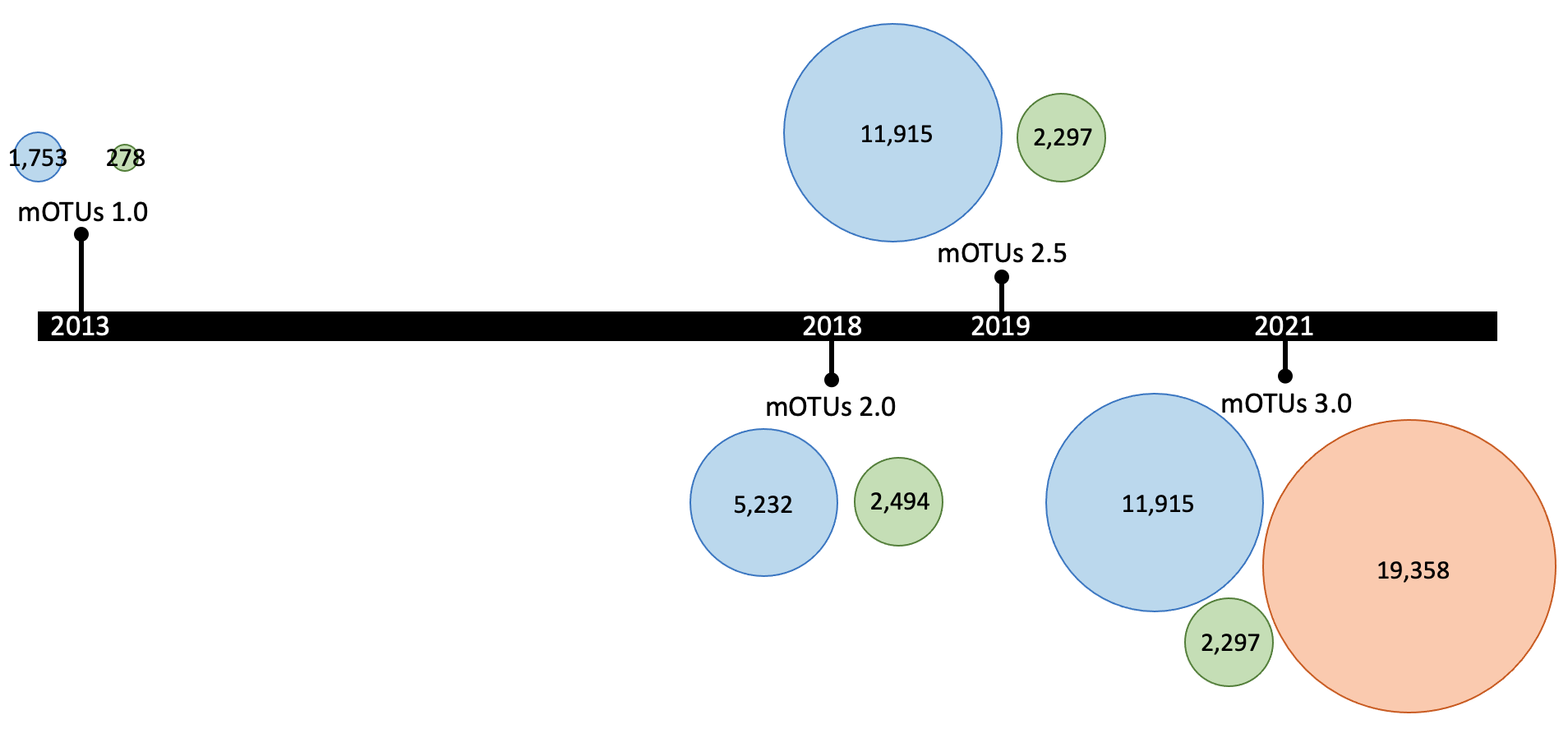
The mOTUs database undergoes regular updates. Major releases are depicted in the graph below, showing the number of mOTUs for each of the three groups, indicated by the same color-coding as the previous graph.
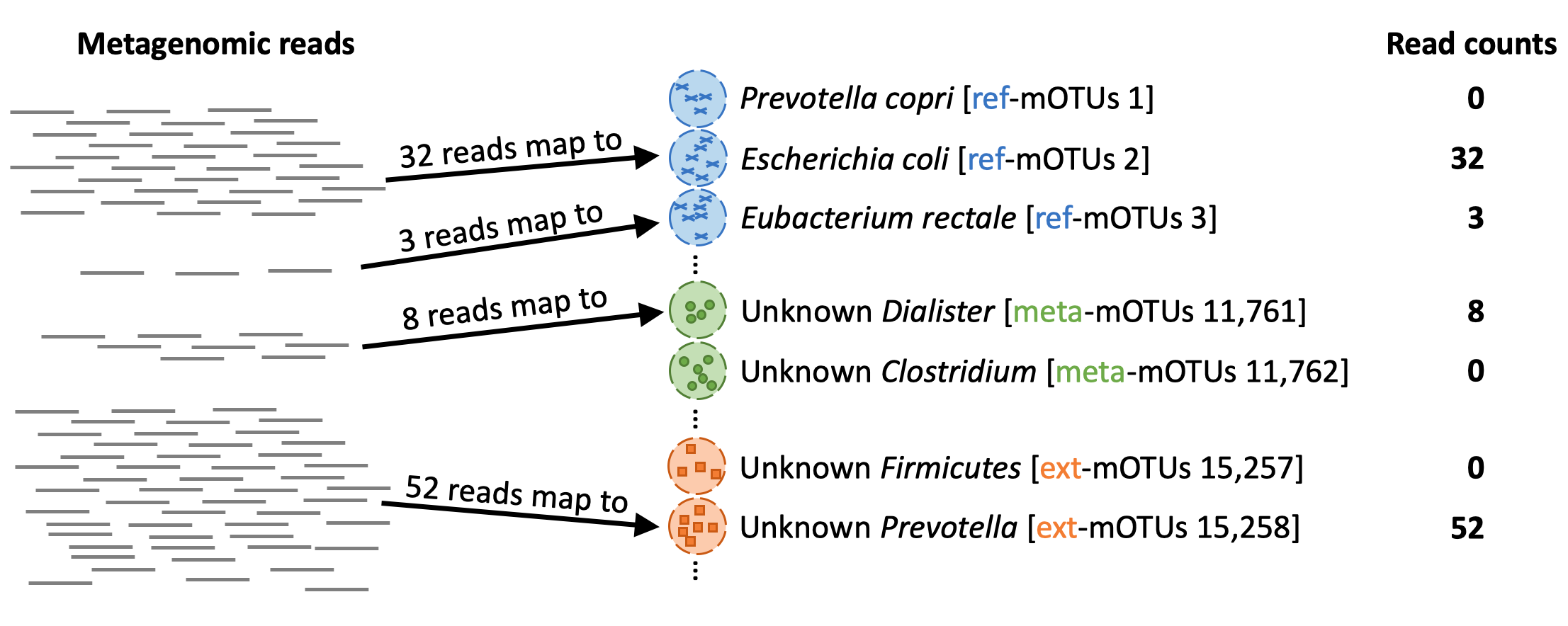
When profiling (motus profile) a metagenomic sample, the mOTUs tool maps the reads from the sample to the genes in the different mOTUs:
mOTUs marker genes¶
The mOTUs tool utilizes a set of 10 single-copy universal marker genes as a basis for its analysis:
Gene family |
Description |
|---|---|
COG0012 |
Predicted GTPase, probable translation factor |
COG0016 |
Phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase alpha subunit |
COG0018 |
Arginyl-tRNA synthetase |
COG0172 |
Seryl-tRNA synthetase |
COG0215 |
Cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase |
COG0495 |
Leucyl-tRNA synthetase |
COG0525 |
Valyl-tRNA synthetase |
COG0533 |
Metal-dependent proteases with possible chaperone activity |
COG0541 |
Signal recognition particle GTPase (Ffh) |
COG0552 |
Signal recognition particle GTPase (FtsY) |
